Introduction
Overview
The Logic Analyzer API (also referred to as IHWAPI, which is a - legacy - short term for Ikalogic Hardware API) is a collection of libraries (DLLs for Windows, SO files for Linux/macOS) that allows users to interface with Ikalogic's logic analyzer devices programmatically.
This API is designed for seamless integration with various programming languages and environments, including C, C++, C#, and Visual Basic, thanks to its ABI compatibility. However, official support is currently provided only through C header files. If additional language bindings are required, we welcome feedback on possible expansions.
The API maintains a consistent structure across different devices to ensure a unified experience. However, due to inherent hardware differences, some variations in functionality may exist.
Ikalogic logic analyzer devices are designed to operate using ScanaStudio software. While it's possible to achieve equivalent signal capture results using the API, the signal generation features as well as advanced trigger features are only available via ScanaStudio for the time being.
API Workflow
The typical workflow for interacting with a logic analyzer using the API follows these steps:
- Detect available devices – List all connected devices on the USB bus.
- Open a device – Select and open a device from the available list.
- Configure and start a capture – Set up the analyzer and begin data acquisition.
- Retrieve captured samples – Access and process the recorded signal data.
- Close the device – (Optional) Close the device when finished.
Closing the device after retrieving data is not mandatory. If multiple captures are needed, the device can remain open for extended use. Additionally, the API provides functions to poll the connection status, ensuring the device remains available before initiating new captures.
Retrieving Captured Samples
As of API version 2.0, the sample retrieval mechanism has been redesigned to align with the ScanaStudio scripting API. Captured signals are stored in a compressed format, significantly optimizing memory usage.
Instead of storing every individual sample, only logic transitions are recorded. Each transition consists of:
- Transition value (logic level change)
- Sample index (position in the timeline)
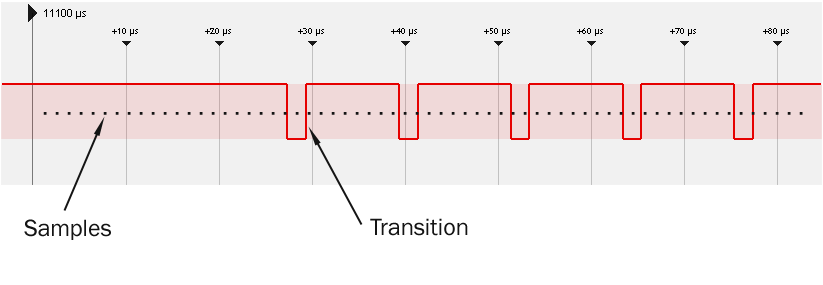
Processing Transitions
Internally, each logic channel maintains an iterator that retrieves stored transitions efficiently. Before reading transitions, the iterator must be reset using the appropriate API function:
- SP259 series
- SP1000G series
- SP209 series
sp259api_trs_reset(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
sp1000gapi_trs_reset(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
sp209api_trs_reset(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
Subsequently, the transitions are retrieved sequentially using:
- SP259 series
- SP1000G series
- SP209 series
sp259api_trs_get_next(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
sp1000gapi_trs_get_next(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
sp209api_trs_get_next(); // Resets iterator to the first transition
until the last transition is reached.
Under the hood, the API have an iterator attached to each logic channel. The job of the iterator is to fetch the logic transitions (i.e. logic change) from the compressed storage, and provide it the user of the API, in the most efficient way (offering very fast fetching with minimal memory and processor impact). As with the scripting API, the iterator for each channel needs to be reset, before it can be used to navigate to the first transition. (using the function DEVICEAPI_trs_reset() or DEVICEAPI_trs_before(), where DEVICEAPI_ is to be replaced with your actual device api name like in the examples above).
Then, the proper way to retrieve captured samples is to call DEVICEAPI_trs_next() until the very last transition is reached for a specific channel.
Example: Retrieving Captured Samples
The following is a example showing how to open a device, launch a capture and retrieve captured samples (C++ Code). Please note that this code is rather a simplistic minimal example than a recommended way of interfacing to the device. Please refer to the dedicated chapter of each device for detailed API reference.
- SP259 series
- SP1000G series
int main()
{
sp259api_handle h;
sp259api_create_new_handle(&h, sp259api_model_t::sp259_industrial);
sp259api_create_device_list(h);
sp259api_device_open_first(h);
sp259api_free_device_list(h);
sp259api_settings_t settings = {};
settings.sampling_depth = 10e6;
settings.post_trig_depth = settings.sampling_depth * 0.9;
settings.s_clk = 250e6;
sp259api_trigger_description_t trig_a, trig_b;
trig_a.type = sp259api_trigger_type_t::SP259API_TRG_NOTRIG;
trig_a.channel = -1;
trig_b.type = sp259api_trigger_type_t::SP259API_TRG_NOTRIG;
trig_b.channel = -1;
sp259api_launch_new_capture_simple_trigger(h, trig_a, trig_b, settings);
int64_t total = 0; //total samples
int64_t pre = 0; //pre trigger samples
int64_t post = 0; //post trigger samples
while (post < settings.post_trig_depth)
{
e = sp259api_get_available_samples(h, &total, &post);
pre = total - post;
msleep(100);
std::cout << "retrieved transitions, pre-trig: " << pre / 1000 << +" K, post-trig:" << post / 1000 << " K" << std::endl;
}
const uint8_t ch = 1;
sp259api_trs_t trs;
sp259api_trs_reset(h, ch);
trs.sampple_index = 0;
bool is_not_last = true;
int trs_count = 0;
while (is_not_last && trs_count < 10)
{
sp259api_trs_get_next(h, ch, &trs);
printf("TRS @ %lld [%d]\n", trs.sampple_index, trs.value);
sp259api_trs_is_not_last(h, ch, &is_not_last);
trs_count++;
}
sp259api_free(h);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
sp1000gapi_handle h;
sp1000gapi_create_new_handle(&h, sp1000gapi_model_t::sp1054g);
sp1000gapi_create_device_list(h);
sp1000gapi_device_open_first(h);
sp1000gapi_settings_t settings = {};
settings.s_clk = 250e6;
settings.sampling_depth = 10e6;
settings.post_trig_depth = settings.sampling_depth * 0.9;
settings.thresh_capture_mv[0] = 1000;
settings.ext_trig_out_polarity = true;
for (int ch = 0; ch < SP1000G_CHANNELS_COUNT; ch++) {
settings.io_type[ch] = SP1000GAPI_IO_IN;
settings.io_pull[ch] = SP1000GAPI_PULL_DOWN;
}
sp1000gapi_trigger_description_t trig_a = {SP1000GAPI_TRG_NOTRIG, -1};
sp1000gapi_trigger_description_t trig_b = {SP1000GAPI_TRG_NOTRIG, -1};
sp1000gapi_launch_new_capture_simple_trigger(h, trig_a, trig_b, settings);
int64_t total_samples = 0, post_trig_samples = 0;
while (post_trig_samples < settings.post_trig_depth) {
sp1000gapi_get_available_samples(h, &total_samples, &post_trig_samples);
msleep(100);
}
const uint8_t ch = 1;
sp1000gapi_trs_t trs;
sp1000gapi_trs_reset(h, ch);
trs.sampple_index = 0;
bool is_not_last = true;
int trs_count = 0;
while (is_not_last && trs_count < 10)
{
sp1000gapi_trs_get_next(h, ch, &trs);
printf("TRS @ %lld [%d]\n", trs.sampple_index, trs.value);
sp1000gapi_trs_is_not_last(h, ch, &is_not_last);
trs_count++;
}
sp1000gapi_free(h);
return 0;
}
Header Files
To use the API, the following header files must be included in the project:
-
ihwapi_common_types.h- Shared across all logic analyzer devices.
- Defines core types and structures used throughout the API.
-
*DEVICE*_types.h- Contains device-specific type definitions and structures.
*DEVICE*should be replaced with the actual device name (e.g.,sp209_types.h).
-
*DEVICE*api.h- Declares all API functions for the specific logic analyzer model.
Thread Safety
Unless explicitly stated otherwise, all API functions are thread-safe, ensuring safe execution in multi-threaded environments.
This document assumes you have some general programming knowledge, specially in C / C++